Linear Servo Motors
World's Largest Supplier of Linear Servo Motors
Linear motors come in a variety of technologies and styles, including brush or brushless, and configured as flat iron-core, U-shaped, or tubular. Nippon Pulse’s tubular Linear Servo Motor consists of a magnetic shaft and coil assembly (forcer) which can be integrated into a mechanical assembly and driven with a brushless DC servo drive. These linear motor actuators can replace ball and lead screw, pneumatic, and conventional flat or U-Channel linear actuation systems.
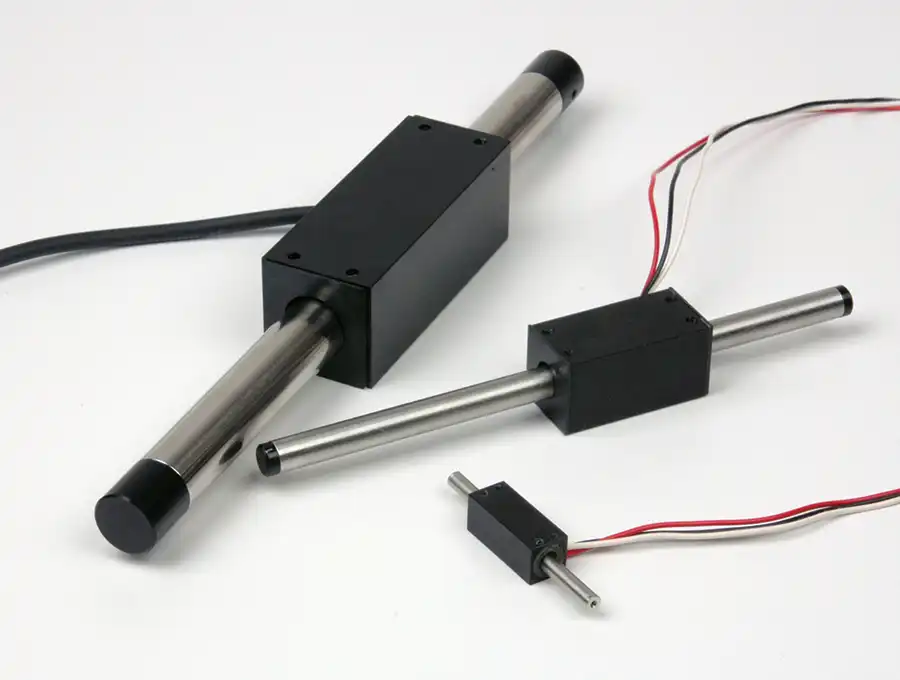

Specification Overview
- Range of shaft diameters: 4mm to 100mm
- Stroke lengths: 20mm to 4.6M
- Achievable peak forces more than 3000N
- Continuous force up to 600N
Linear Servo Motor Advantages
- Simplicity - The simple structure of a magnetic shaft and coil assembly (forcer) experiences minimal wear and is entirely maintenance-free, keeping your
machinery running longer with less downtime and a significant cost reduction throughout its lifespan. - Precision - With no iron in the forcer or shaft, ultra-high precision is achievable with zero cogging for applications that require extreme smoothness of
motion in machine operation. - Accuracy - High-performance positioning with encoder resolutions less than 10nm enable a positioning accuracy of ±1.2 pulses of encoder resolution for
improved yield of high precision processes. - Strength - Rare-earth magnets, the strongest magnets available, add to the intensity of the magnetic field and thus allowing a small amount of current to
produce large amounts of force for low power and high efficiency machines. - Speed - Able to efficiently move large amounts of weight accurately and smoothly at high speeds, increasing throughput and profitability.
Precision Solutions for Industries
- Packaging
- Life Sciences
- Semiconductor
- Optics & Photonics
- Robotics
- Toolless Cutting
- Lab Automation
- Pharmaceuticals






How to Select the Best Linear Servo Motor Actuator for your Application
- Outline the motions that you’re trying to achieve
- Find the acceleration traverse and deceleration times need for each movement
- Specify the time between each movement
- Average the force/current needed for all of the moves (RMS average)
- Find a shaft motor with an RMS Force or RMS current larger than what is needed for your move
- Find a power supply and amplifier that can provide the currents needed for your moves (peak and RMS currents)
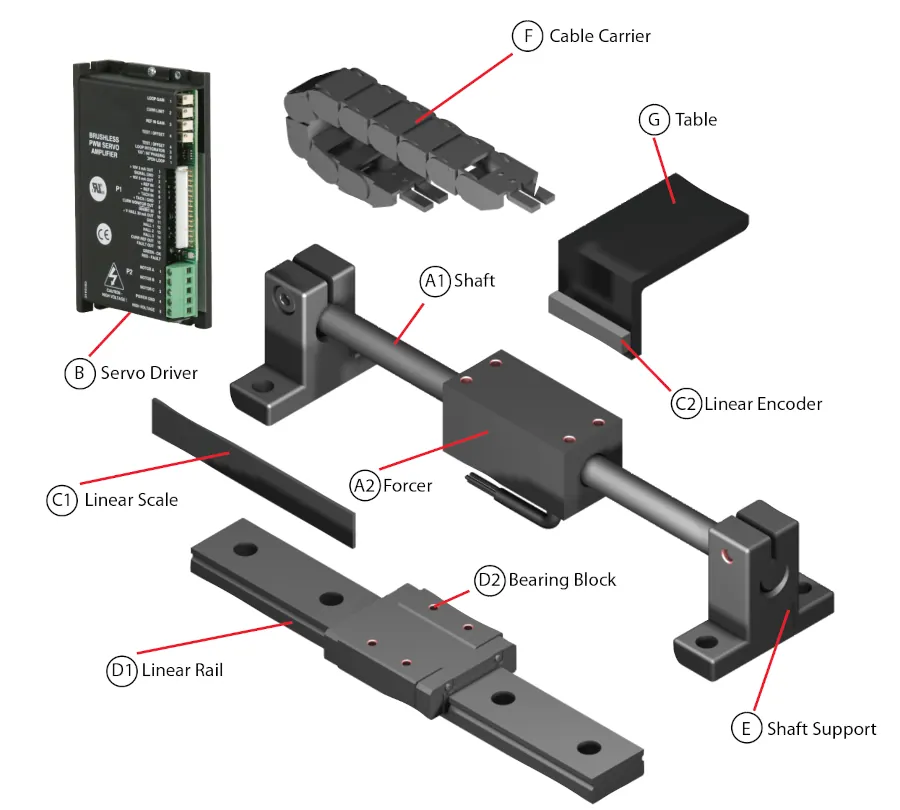
How to Configure a Linear Servo Motor
To configure a system using the Linear Servo Motor, the following peripheral devices are
required:
A1. Linear Servo Motor Shaft – Stainless steel Shaft with embedded magnets
A2. Linear Servo Motor Forcer – Motor coils and hall effects (optional)
B. Servo Driver – Servo amplifier to commutate and control the linear motor
C1. Linear Encoder Scale (optical or magnetic) – Feedback scale
C2. Linear Encoder Read Head – Feedback sensor
D1. Linear Rail – profile or round rail to support the forcer
D2. Linear Bearing Block – Attaches forcer to the bearing rails
E. Shaft Support – used to support the shaft
F. Cable Carrier – supports the cables that mover\ with the forcer
G. Table or Load Plate – mounting surface for the load
Item D1, D2 (Linear Guide) are a necessary part of a system, and must be selected based on the specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and fitted appropriately to the moving element (forcer or shaft).