Linear Stepper Motors
A Simple Solution at a Fraction of the Cost
Nippon Pulse's linear stepper motor is designed to provide a simple tin-can linear actuator at a fraction of the cost of a conventional rotary-to-linear stepper system.
Nippon Pulse's tin-can linear stepper motors have multiple customization options available.
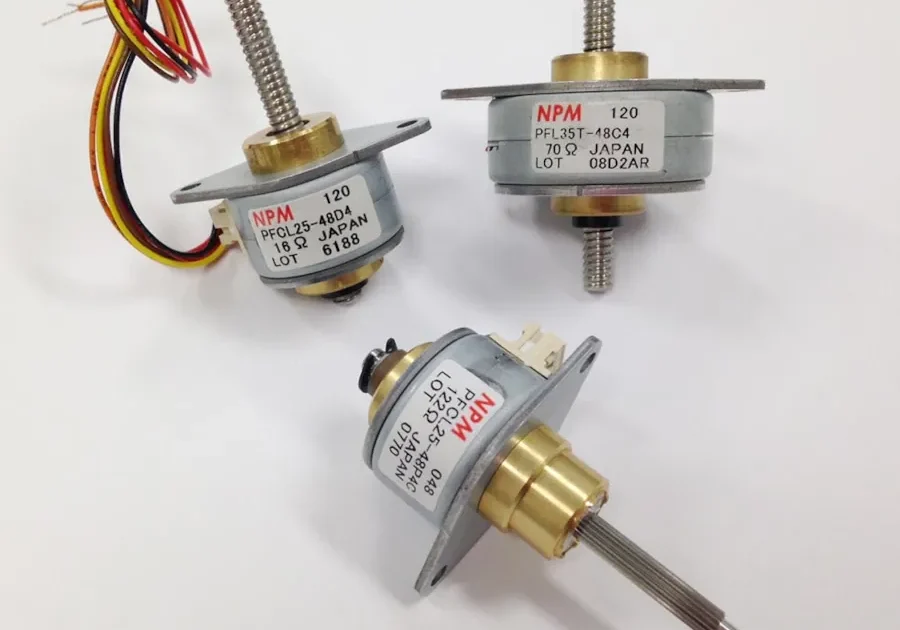

Specification Overview
- Available diameters: 20mm, 25mm and 35mm
- Thread pitches on the lead screw: 0.48mm, 0.96mm, and 1.2mm
- Rated force: Between 8 and 45N
- Effective strokes: 30mm and 60mm
- Rated voltage: 5V and 12V
- 24 or 48 steps per revolution
- Travel/step between 0.01mm and 0.05mm
- Unipolar and bipolar windings
Linear Stepper Motor Advantages
- Flexibility to match application requirements
- Speed, which is easily determined and controlled (speed = steps per revolution /pulse rate)
- Fine incremental moves, which don't require a feedback encoder (open loop)
- Fast acceleration with non-cumulative positioning error
- Low speed/high torque characteristics without gear reduction
- Holds loads in a stationary position without creating overheating
- Wide speed range
Precision Solutions for Industries
- Packaging
- Life Sciences
- Semiconductor
- Optics & Photonics
- Robotics
- Toolless Cutting
- Lab Automation
- Pharmaceuticals






Select the Best Linear Stepper Motor for your Application
- Outline the motions that you're trying to achieve
- Find the acceleration traverse and deceleration times needed for each movement
- Calculate the forces needed to move the payload in the above motion profile
- Find a coil that has a torque curve that provides more force at each speed in your move than is needed to move the payload
- Select the correct electronics needed to drive the motor